| Print|Rate this content |
Standard memory2GB PC2-5300 Fully Buffered DIMMs (DDR2-667) (2 x 1GB) Upgrading memory and memory interleavingWhen upgrading memory, DIMMs 1A and 3A must match. DIMMs 5B and 7B, DIMMs 2C and 4C, and DIMMs 6D and 8D must match and must be installed as a pair. When DIMMs 1A and 3A are populated the system is automatically configured for 2:1 interleaving. When all 4 banks are populated the system is automatically configured for 4:1 interleaving. When four, six, or eight DIMMs are populated with identical DIMMs the system is automatically configured for bank interleaving. Standard memory plus optional memoryUp to 50GB memory is available with the standard memory and the optional installation of PC2-5300 Fully Buffered DIMMs (DDR2-667) memory kits. Standard memory replaced with optional memoryUp to 64GB of memory is available with the removal of the standard memory and the optional installation of PC2-5300 Full Buffered DIMMs (DDR2-667) memory kits.
NOTE:
Memory optionsThis server contains eight FBDIMM slots. The server memory can be extended by installing supported Registered DDR-2 FBDIMMs. Memory configurationsThe server supports the following Advanced Memory Protection (AMP) options to optimize server availability.
Maximum memory capacities for all AMP modes will increase with the availability of 4GB and 8GB FBDIMMs, including a maximum of 64GB in Advanced ECC mode. For the latest memory configuration information, refer to the QuickSpecs on the HPE website. Click here to view the HP ProLiant DL380 Generation 5 (G5) QuickSpecs. The Advanced Memory Protection option is configured in RBSU. By default, the server is set to Advanced ECC mode. For more information, refer to HP ROM-Based Setup Utility. If the configured AMP mode is not supported by the installed FBDIMM configuration, the system boots in Advanced ECC mode. The following configuration requirements apply to all AMP modes:
The memory subsystem for this server is divided into two branches. Each memory branch is essentially a separate memory controller. The FBDIMMs map to the two branches as indicated in the following table:
<---– Front of Server
This multi-branch architecture provides enhanced performance in Advanced ECC mode. The concept of multiple branches is important for the operation of online spare mode and mirrored memory mode. If the server contains more than 4GB of memory, consult the operating system documentation about accessing the full amount of installed memory. Advanced ECC memoryAdvanced ECC memory is the default memory protection mode for this server. In Advanced ECC, the server is protected against correctable memory errors. The server provides notification if the level of correctable errors exceeds a pre-defined threshold rate. The server does not fail because of correctable memory errors. Advanced ECC provides additional protection over Standard ECC because it is possible to correct certain memory errors that would otherwise be uncorrectable and result in a server failure. Whereas standard ECC can correct single-bit memory errors, Advanced ECC can correct single-bit memory errors and multi-bit memory errors if all failed bits are on the same DRAM device on the FBDIMM. In addition to general configuration requirements, Advanced ECC memory also has the following configuration requirements:
In Advanced ECC mode, FBDIMMs must be populated as specified in the following table:
Online spare memory configurationOnline spare memory provides protection against degrading FBDIMMs by reducing the likelihood of uncorrectable memory errors. This protection is available without any operating system support. An understanding of single-rank and dual-rank FBDIMMs is required to understand memory usage in online spare mode. FBDIMMs can either be single-rank or dual-rank. Certain FBDIMM configuration requirements are based on these classifications. A dual-rank FBDIMM is similar to having two single-rank FBDIMMs on the same module. Although only a single FBDIMM module, a dual-rank FBDIMM acts as two separate FBDIMMs. The purpose of dual-rank FBDIMMs is to provide the largest capacity FBDIMM for the current DRAM technology. If the current DRAM technology allows for 2GB single-rank FBDIMMs, a dual-rank FBDIMM using the same technology would be 4GB. In online spare mode, a single rank of memory acts as the spare memory. For single-rank FBDIMMs, the entire FBDIMM acts as the spare memory. For a dual-rank FBDIMM, only half of the FBDIMM acts as the spare memory while the other half is available for operating system and application usage. If one of the non-spare FBDIMMs receives correctable memory errors at a higher rate than a specific threshold, the server automatically copies the memory contents of the degraded rank to the online spare rank. The server then deactivates the failing rank and automatically switches over to the online spare. Because FBDIMMs that experience a high rate of correctable memory errors also have a higher probability of receiving an uncorrectable memory error, this configuration reduces the likelihood of uncorrectable memory errors that would result in server downtime. Online spare is performed per branch of the memory controller. For a server with both branches populated, two ranks are used for online spare memory. One branch can fail over to the associated online spare while the other branch is still protected. Each branch is made up of two banks:
Online spare FBDIMM configuration requirements (in addition to general configuration requirements):
In online spare mode, FBDIMMs must be populated as specified in the following table:
After installing FBDIMMs, use RBSU to configure the system for online spare memory support. Mirrored memory configurationMirroring provides protection against uncorrectable memory errors that would otherwise result in server downtime. Mirroring is performed on the branch level. Branch 0 and branch 1 mirror each other. Each branch maintains a copy of all memory contents. Memory writes go to both branches. Memory reads come from only one of the two branches (unless an uncorrectable error occurs). If a memory read on one branch returns incorrect data due to an uncorrectable memory error, the system automatically retrieves the proper data from the other branch. A branch is not necessarily disabled (thus losing mirroring protection) because of a single uncorrectable error. Mirroring protection is not lost because of transient and soft uncorrectable errors, resulting in systems that maintain mirroring protection (and thus improved uptime) unless there is a failure of both branches. Mirrored memory FBDIMM configuration requirements (in addition to general configuration requirements):
When using mirrored memory mode, FBDIMMs must be populated as specified in the following table:
After installing FBDIMMs, use RBSU to configure the system for mirrored memory support. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mac Pro (2019) has 12 DIMM (memory) slots that support up to 1.5TB of 2933MHz memory when all 12 slots are full using DDR4 ECC DIMMs. 8-core, 12-core, and 16-core Mac Pro models support up to 768GB of memory.
Legal Disclaimer: Products sold prior to the November 1, 2015 separation of Hewlett-Packard Company into Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company and HP Inc. may have older product names and model numbers that differ from current models.
Provide feedback |
| Please rate the information on this page to help us improve our content. Thank you! |
- Was the information on this page helpful?
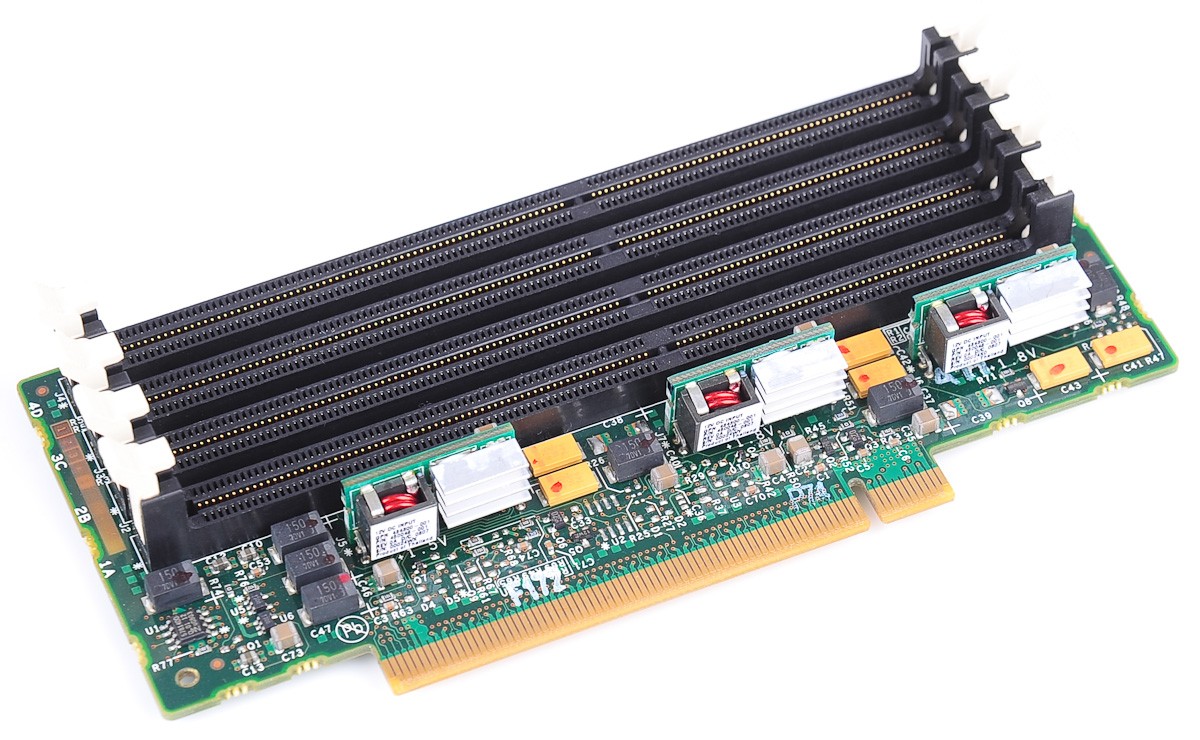
Mac Pro has a 6-channel memory controller that supports 12 memory slots you can use to install up to 1.5TB of memory using 2933MHz DDR4 ECC compliant memory DIMMs. To ensure compatibility, Apple recommends that you use Apple-approved memory. You can purchase Apple-approved memory online from the Apple Store or by visiting an Apple Retail Store or Apple Authorized Reseller.
Memory requirements
When you upgrade the memory in your Mac Pro, it must meet these requirements:
- 2933MHz DDR4 full-length DIMM. Mixing memory speeds is not recommended.
- Error-correcting code (ECC)
- 8GB, 16GB, 32GB, 64GB, or 128GB DIMMs
- Registered (R-DIMM) or Load-Reduced DIMM (LR-DIMM). Do not mix R-DIMMs and LR-DIMMs.
- 288-pin
- Use the same size memory modules across all slots to maximize performance.
- DIMMs with heatsinks are not supported and may damage the DIMM mechanism.
The Mac Pro supports both R-DIMMs and LR-DIMMs, but you can't mix these two memory types. Mixing R-DIMMs and LR-DIMMs will result in a memory error flash of the status indicator light when you turn on your computer.
Ecc Memory Vs Non Ecc
Model specifications
| Mac Pro model | Max RAM | Speed | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8-core | 768GB | 2666MHz DDR4 ECC | LR-DIMM or R-DIMM |
| 12-core | 768GB | 2933MHz DDR4 ECC | LR-DIMM or R-DIMM |
| 16-core | 768GB | 2933MHz DDR4 ECC | LR-DIMM or R-DIMM |
| 24-core | 1.5TB | 2933MHz DDR4 ECC | LR-DIMM or R-DIMM |
| 28-core | 1.5TB | 2933MHz DDR4 ECC | LR-DIMM or R-DIMM |
Configured from Apple, Mac Pro models include the following DIMM types:
- R-DIMMs for configurations up to 192GB (6x32GB).
- LR-DIMMs for configurations of 384GB (6x64GB) or more.
Who Needs Ecc Memory
All memory included with your Mac Pro is 2933MHz. Mac Pro models with 8 core processors operate memory at 2666MHz.
Comments are closed.